Mong Ton
ဝဵင်းမိူင်းတူၼ် မိုင်းတုံမြို့ | |
|---|---|
Town | |
| Coordinates: 20°18′N 98°56′E / 20.300°N 98.933°E | |
| Country | |
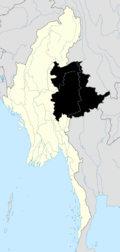
| State | |
| District | Mong Ton District |
| Township | Mong Ton Township |
| Elevation | 1,612 ft (491 m) |
| Population | About 90,000 |
| Time zone | UTC+6:30 (MMT) |
Mong Ton (Burmese: မိုင်းတုံမြို့, MLCTS: muing.tu.mrui) also known historically as Möngtung and Maington, is the capital of Mong Ton District and seat of Mong Ton Township southern Shan State in eastern Myanmar near the border with Thailand. Mong is equivalent to Township or land."Ton"is equivalent to [Royal City].[1] It is located in the Daen Lao Range, in the eastern part of the Shan State, east of the Salween River. Mong Ton lies on the National Highway 22 and connected to NarrkgMuu and Ponparkyin, is also connected to Mong Hsat by National Highway 49 which begins to the north-east of the town.[2]
History
[edit]Mong Ton has had a turbulent and unstable history.[3] According to Shan tradition King Naresuan was cremated and his ashes interred in a stupa in Mong Ton.[4] in 1888, when the area was part of British Burma, Möngtung, Möng Hang, Möng Hat and Möng Kyawt, were claimed by Siam and were occupied secretly by Siamese troops. A fifth district, Möng Hsat, was also claimed by Siam, but no garrisons were posted there.[5] The districts were annexed by Thailand in 1942, following the Japanese invasion of Burma and were added to the Saharat Thai Doem territory. They were returned to British Burma at the end of World War II.[6]
More recently there have been conflicts between the Shan State Army – South (SSA-S) and the Myanmar Armed Forces, although the problem is worse in the Kyethi, Mongkung, and Laihka Townships.[7] In Mong Ton and Mong Hsat Township, the SPDC has demanded the removal of some UWSA military outposts and the Burmese Army is exerting more pressure on Lahu militias to conscript more soldiers and prepare to fight both the SSA–S and the UWSA.[7] The SPDC supported three basic military training courses for the Lahu militia in Mong Ton during 2009.[7]
Given its location near the border with Thailand and internal conflict, the Myanmar Armed Forces have the important IB277 military base just outside the town. There are five Burmese army battalions in Mong Ton town alone.[8] Trafficking of narcotics is a major problem in Mong Ton and Burma is the number two opium producer in the world after Afghanistan, and one of the leading producers of amphetamines in South East Asia.[8] The Free Burma Rangers have alleged that the army is involved in the production and trafficking of narcotics in order to profit from the trade in opium, heroin and amphetamines.[8] Opium is cultivated and it is not only processed for trade abroad it is also consumed by some local villagers and has created drug addiction problems.[8]
In April 2022, it was split from Mong Hsat District to form its own district - Mong Ton District.[9]
References
[edit]- ^ "Mong Ton (MGK) Myanmar". www.world-airport-codes.com. Archived from the original on March 16, 2006.
- ^ "Mong Ton Map — Satellite Images of Mong Ton". Archived from the original on September 6, 2012.
- ^ Lintner, Bertil (1994). Burma in revolt: opium and insurgency since 1948. Westview Press. p. 224. ISBN 978-0-8133-2344-2.
- ^ Subhatra Bhumiprabhas (April 30, 2006). "Warrior king remains a very modern mystery". The Nation. Archived from the original on June 17, 2011.
- ^ "The Pacification of Burma, by Sir Charles Haukes Todd Crosthwaite". www.gutenberg.org. Archived from the original on November 21, 2014.
- ^ "Thailand?". Axishistory.com. November 20, 2005. Archived from the original on August 29, 2014.
- ^ a b c "Southern Shan State". Thailand Burma Border Consortium. Archived from the original on March 28, 2010. Retrieved February 28, 2010.
- ^ a b c d "Oppression: Burma Army Militarization and the Use of Proxies in Eastern Shan State". www.taigress.info. July 23, 2008. Archived from the original on November 21, 2008.
- ^ "Expansion of new districts: New districts expanded in Nay Pyi Taw, regions and states". Myanmar International Television. May 2, 2022. Archived from the original on March 14, 2023.